Checked Exception과 UnCheckedException의 차이점 정리 및 실험
Checked Exception 과 UnCheckedException의 차이
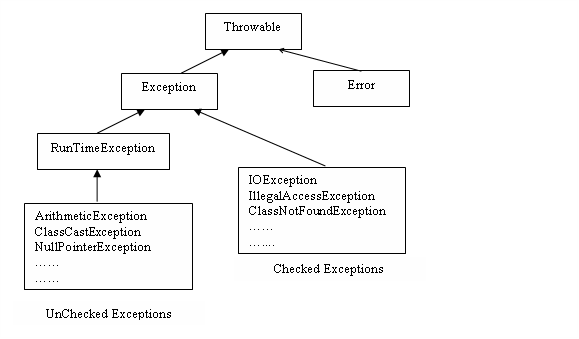
- Checked Exeption
- 어플리케이션에서 반드시 예외 처리를 해야 한다. 하지 않을시 Runtime Error 가 발생
- Transaction Rollback이 되지 않는다.
- 대표적으로 IO,SQLException이 있다.
- try-catch 로 예외를 처리 하거나 상위 메소드로 예외 처리로직을 위임 할 수 있다.
- UnCheckedException
- 어플리케이션에서 예외처리를 강제 하지 않는 에러.
- Transaction Rollback 처리
- 대표적으로 Runtime Exception, NullPointer, IllegalArgumentException 등이 존재 한다.
- 명시적 예외 처리 로직이 필요하지 않는 에러
- 두가지 Exception을 나누는 기준은 위 표와 같이 Runtime Exception의 상속 여부 이다.
- RuntimeException 을 상속받는 Exception 모두가 Unchecked Exception이라고 할 수 있다.
- 간단한 예시를 통하여 Unchecked Exception 의 Rollback을 확인해보자.
1 | |
위와 같이 Service 로직에서 데이터를 저장 후 Unchecked Exception 을 던지게 되면 어떤 일이 일어날지 간단한 테스트 실행.
1 | |
-
위 로그를 보시면 UncheckedException 이 발생하면 rollback 이 정상적으로 일어난 것을 확인 할 수 있습니다.
-
CheckedException이 발생 하였을때 정말 Rollback이 되지 않을까 ?
마찬가지로 간단한 테스트를 실행해보자.
1 | |
User를 저장하고 강제로 Exception을 던져보았습니다.
1 | |
- 위 로그를 보시면 정상적으로 CheckedException이 발생 하였지만
m.s.q.exceptiontest.service.UserService : throw exceptionUser 데이터가 저장되는것을 확인 할 수 있습니다. - CheckedException 이 발생 될 때 정상적으로 Rollback을 하기 위한 여러가지 방법이 있지만 저는 명시적인 UncheckedExecption을 던져주는 방식으로 Rollback이 되는지 실행 해보겠습니다.
1 | |
위 코드와 같이 CheckedException 이 던져질 경우 catch에서 명시적인 예외를 다시 던져주는 방식으로 실행 해 보겠습니다.
1 | |
위 로그와 같이 명시적인 에러를 던져줌으로서 정상적으로 Rollback이 되는것을 확인 할 수 있습니다.
Exception의 종류에 따라 트랜젝션 여부가 다르다는것을 알고 있었지만 실제로 어떻게 처리하는지, 정말 Rollback이 안되는지 등에 대한 실행을 통한 결과 검증 과정을 정리 하였습니다.
지금까지 Exception 처리시 별다른 처리를 하지 않고 단순 로그만 남기는 경우가 많이 있었는데 이번 테스트를 통하여 정확한 예외 처리 방법에 대한 학습을 할 수 있었습니다. :)
참고
- https://cheese10yun.github.io/checked-exception/
- https://1.bp.blogspot.com/